While the United States is just beginning to catch up with the legalization of cannabis, scientific studies have been exploring how and why cannabis compounds affect humans the way they do. This led to the discovery and exploration of the endocannabinoid system (ECS). A thorough understanding of how cannabinoids interact with the ECS and the way the ECS influences several bodily processes can help you tap into a deeper cannabis experience.
What Is the Endocannabinoid System?
The endocannabinoid system is a complex cell-signaling system with many functions, all tied to maintaining homeostasis, or a balanced internal environment, in the body. The ECS is found in all mammals, not just humans, and helps to maintain homeostasis in the body by regulating many physiological processes. These processes are vital for the function of the body and include pain reduction, appetite, memory, and mood.
The ECS was discovered in the early 1990s as researchers studied the way THC interacts with receptors in the body. They found that ECS receptors are designed to interact with endocannabinoids, biological compounds created in the body that are structured very similarly to the cannabinoids found in cannabis. Because they are structurally similar, cannabis cannabinoids are also capable of interacting with ECS receptors.
Let’s dive deeper into the main components of the endocannabinoid system.
Endocannabinoids
Endocannabinoid molecules, also called endogenous cannabinoids, have a structure much like the cannabinoids found in cannabis itself. However, they are naturally produced within all mammalian bodies. More specifically, endocannabinoids are lipid-based neurotransmitters that send signals between nerve cells to aid in various bodily functions.
The body produces endocannabinoids as they are needed to maintain balance within the body. As a result, typical levels of these compounds are unknown unless homeostasis is disturbed. Experts have identified two key endocannabinoids thus far: anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol.
Naturally produced endocannabinoids are present in the brain, muscle, circulating cells, other tissues, and organs. Meanwhile, the plant-based cannabinoid THC is exclusively found in cannabis—though researchers have recently identified other cannabinoids in other plants. These compounds become active when they bind to the active site on a cannabinoid receptor. Though the exact mechanism that triggers or promotes endocannabinoid binding is unknown, it is theorized that the binding occurs when a system in the body is out of balance and needs correcting.
Endocannabinoid Receptors
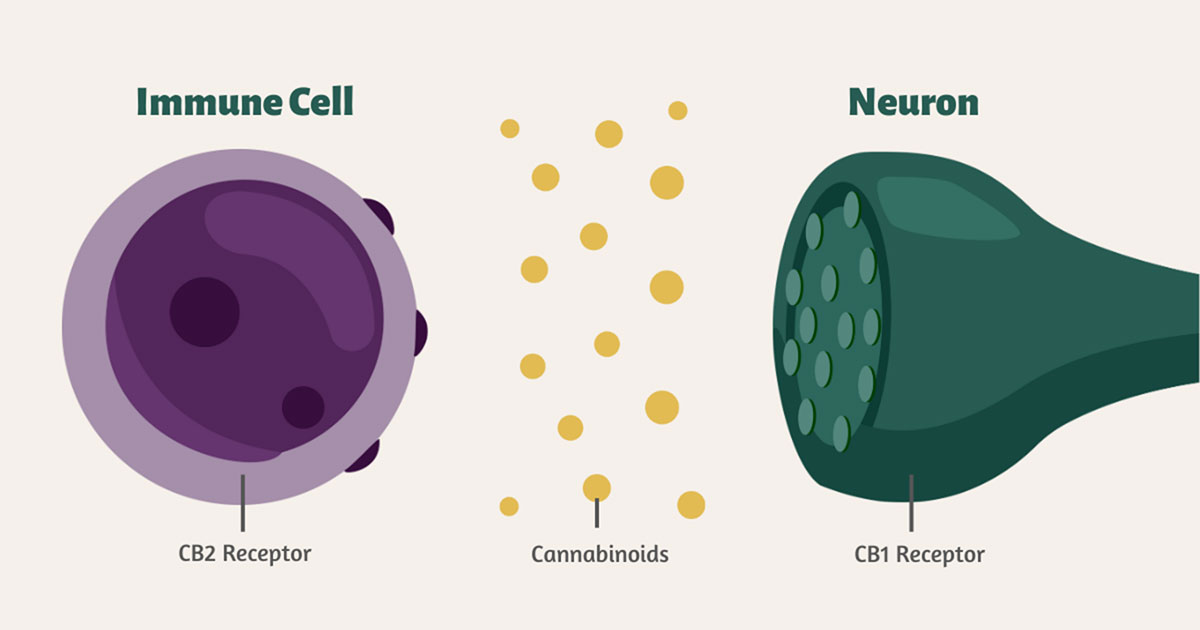
ECS chemical receptors are located on the surface of cells throughout the body, most notably in the brain, central nervous system, and peripheral nervous system. Researchers have also identified critical ECS receptors in the gut, as well as other critical bodily systems. No matter their location, endocannabinoids chemically bind with these receptors and send a chemical message to the endocannabinoid system, kickstarting the corresponding response.
The two primary receptors throughout the body are CB1 and CB2 receptors. CB1 receptors reside in the central nervous system and affect motor and cognitive function, while CB2 receptors in the peripheral nervous system affect neuroprotection and neuroinflammation. CB1 receptors modulate most of the psychoactive effects of cannabinoids, while CB2 receptors deal with the other physiological responses.
Enzymes
Enzymes are complex molecules required for most chemical processes in the body. They are responsible for instigating and speeding up reactions as well as breaking down molecules following a reaction. In the ECS, enzymes break down the cannabinoid and endocannabinoid molecules after they carry out their function. The two primary enzymes in the endocannabinoid system are fatty acid amide hydrolase for breaking down anandamide and monoacylglycerol for breaking down 2-arachidonoylglycerol.
What Does the Endocannabinoid System Do?
The ECS is incredibly complex and has only been under study since the mid-1990s. For that reason, we suspect that many potential functions have yet to be determined. However, research has shown a connection between the ECS and the following processes:
- Metabolism
- Appetite and digestion
- Chronic pain
- Mood
- Learning and memory
- Inflammation and other immune responses
- Sleep
- Motor control
- Muscle formation
- Cardiovascular system function
- Bone remodeling and growth
- Liver function
- Stress
- Reproductive system function
- Skin and nerve function
All these functions can affect the homeostasis of the body, and thus, many experts believe maintaining homeostasis is the primary function of the ECS. Homeostasis is vital for the body to function properly, and even minor fluctuations can cause disastrous effects.
What Causes the Endocannabinoid System to Function Improperly?
Failing to maintain a stable internal environment can have severe, systemic effects like illnesses and diseases, cellular toxicity from the accumulation of harmful byproducts and reactive oxygen species, or even organ failure. Research has suggested that ECS dysfunction or low endocannabinoid levels contribute to the development of some health conditions, like fibromyalgia, migraines, and irritable bowel syndrome.
The main cause of ECS dysfunction is an endocannabinoid imbalance. Genetics can play a part in developing an endocannabinoid imbalance, but there are several external factors that also play a role.
These include:
- Prescription medications
- Poor diet
- Stress
- Chronic diseases
How Is Cannabis Relevant to the Endocannabinoid System?
It might be more appropriate to ask how the ECS is relevant to cannabis, as this system was discovered while researchers and scientists were exploring the effects of cannabis on the human body. As noted, some of the compounds discovered in the body were profoundly similar to compounds in cannabis already known as cannabinoids. Therefore the corresponding compounds in the body are called endocannabinoids—endo means within, so endocannabinoids are cannabinoids naturally found within the body.
Both endocannabinoids and cannabinoids interact with the body’s endocannabinoid receptors. Therefore, introducing cannabinoids can enhance or stimulate the ECS or even cause it to work in diverse and new ways. To a certain extent, using cannabis is like supplementing the body with customizable cannabinoid compounds that may specifically target receptors for desired effects. In this way, your body can be influenced to produce therapeutic receptor responses to enhance the body’s homeostasis and achieve a sensory experience.
Cannabinoids and the ECS
While there are over 150 cannabinoids, there are two primary cannabinoids we understand the best. Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) can interact with the ECS, causing the therapeutic and psychoactive effects characteristic of cannabis use.
THC and the ECS
CBD and the ECS
THC is the compound in cannabis that causes most of the sensory feelings characteristic of cannabis. It interacts with the ECS by binding with both CB1 and CB2 receptors. This high affinity for both receptor types allows for a wide range of powerful effects on your body and mind. THC can stimulate your appetite, reduce pain, reduce inhibitions, cause relaxation, and more. It is like the endocannabinoid anandamide and activates the brain’s reward system, causing pleasurable psychoactive effects.
As you may already know, CBD is significantly different from THC. It does not cause the psychoactive effects that THC does but has been shown to have therapeutic effects. CBD reacts with the body differently because it does not appear to bind to known receptors. Instead, it seems to modulate the way THC binds to receptors and may even prevent endocannabinoids from breaking down. Alternatively, CBD may bind to a receptor that is currently undiscovered. Research suggests that the way cannabinoids interact with the ECS can help alleviate symptoms associated with many conditions.
How Cannabinoids Affect the ECS

Research into the effects of cannabinoids on the human body is far from complete, but there is a plethora of anecdotal evidence to show that cannabinoids can be used to treat many conditions.
More research can shed light on how cannabinoids affect the balance of the ECS and help people with these conditions:
- Poor metabolism or appetite
- Insomnia
- Chronic and acute pain
- Opioid addiction and withdrawal
- Anxiety
- Forgetfulness and memory loss
- Depression
- PTSD
Supporting Your Endocannabinoid System
As we mentioned, genetic factors, poor diet, stress, prescription medication, and chronic disease can negatively affect your ECS. So, can cannabis help you restore balance? Anecdotal evidence certainly suggests a positive link. Consider cannabis and other proactive measures to balance the ECS.
THC and CBD
These naturally occurring cannabinoids interact with the endocannabinoid receptors in the brain. CBD especially may cause calming effects, especially for those with anxiety or other chronic ailments. This calming effect both results from ECS regulation and helps restore balance.
Other Phytocannabinoids
Some foods are naturally rich in phytocannabinoids, which can react with the ECS to restore balance in the body. These foods include ginger, chocolate, black pepper, and nutmeg. A diet rich in these foods may help restore balance.
Reduce Excessive Alcohol Use
CB1 receptors can become overactive in people that regularly consume alcohol. When this occurs, fewer receptors are generated by the body, throwing your ECS out of balance. Detoxing from excessive alcohol use could reduce CB1 receptor sensitivity.
Fish Oil
An overactive endocannabinoid system can be the result of sensitive CB1 and CB2 receptors, and affected individuals are prone to an inflammatory reaction. Fish oil is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which can help compensate for an overactive ECS. Endocannabinoids are a product of fatty acids breaking down, and additional endocannabinoids can nullify the hypersensitivity of cannabinoid receptors.
Exercise
Levels of anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglyerol in the blood are increased by a sustained period of physical exertion. This can relieve stress and improve mood, as well as balance the ECS.

Learn More About How and Why Cannabis Affects You
Cannabis use has existed through the ages and was thought by many cultures to balance the body and mind. Though we are just now beginning to understand the science behind the ECS in the modern age, the prospect of restoring balance to the body with cannabinoids is an exciting one.
If you’d like to continue your cannabis education, browse our other topics and deepen your cannabis connection. And, be sure to subscribe to the Dank Budz cannabis news and information blog to stay in touch with the cannabis community.
Explore
Continue Your Cannabis Learning with Dank Budz
Cannabinoids are an essential component of the therapeutic and psychoactive effects most people seek when they consume cannabis. However, they are far from the only important compounds found within our favorite plant. Keep reading to learn more about cannabis science.

